Akiko KOBAYASHI (Univ. Tokyo), Masahiro NAKATA (Univ. Tokyo), Hayao KOBAYASHI, Kazuo TAKIMIYA (Hiroshima Univ.), Tetsuo OTSUBO (Hiroshima Univ.) and Fumio OGURA (Kinki Univ.)
[J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 837 (1997)]
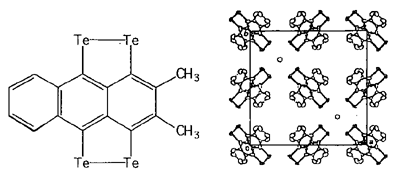
In the field of molecular conductors, systems based on tellurium-containing donor molecules have not received as much attention as systems based on sulfur- or selenium-containing donors. By incorporating heavy chalcogen atoms such as tellurium into donor molecules, a new metallic system with a wider bandwidth and a higher dimensionality is expected to appear. We report here the first examples of cation radical salts of a polyacene donor with peri-ditellurium bridges, 2,3-DMTTeA. The resistivities of all the salts showed semiconducting temperature dependence. However, the Br- salt has quite a high room temperature conductivity (1.3 * 103 S cm-1) and a very low activation energy (0.010 eV). The common feature to all the structures of the salts is the disorder of the donor molecules caused by their unsymmetrical shape. One possible reason why the donor molecules have this orientational disorder may be that the Te ··· Te network is dominant in the construction of the crystal structures.

Figure 1. 2,3-DMTTeA structure and Crystal structure of the Br salt.