Kazumasa UEDA (Osaka Pref. Univ.), Toyonari SUGIMOTO (Osaka Pref. Univ. and IMS), Satoshi ENDO, Naoki TOYOTA, Masakado KOHAMA, Koji YAMAMOTO (Osaka Pref. Univ.), Yusaku SUENAGA, Hiroshi MORIMOTO, Toshiyuki YAMAGUCHI, Megumu MUNAKATA (Kinki Univ.), Nobuyoshi HOSOITO (Kyoto Univ.), Nobuko KANEHISA, Yoshiyuki SHIBAMOTO and Yasushi KAI (Osaka Univ.)
[Chem. Phys. Lett. 261, 295 (1996)]
Ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature was observed in the tetramethylammonium (NMe4+) (Figure 1) and cesium (Cs+) salts of tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) and its radical anion (TCNQ-·) in a molecular ratio of 1:2, as is shown in Figure 2. The saturation magnetizations and coercive forces are 0.79 emu/mol and ca. 300 Oe for (NMe4+·TCNQ-·)·/2TCNQ, and 1.46 emu/mol and ca. 100 Oe for (Cs+·TCNQ-·)·1/2TCNQ, respectively. In contrast, the 1:1 TCNQ/TCNQ-· mixed tetraethylammonium (NEt4+) salt, (NEt4+·TCNQ-·)·TCNQ exhibited no ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature nor at lower temperatures.

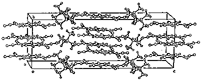
Figure 1. The crystal structure of (NMe4+·TCNQ-·)·1/2TCNQ.
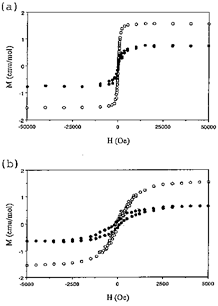
Figure 2. The magnetization curves of (NMe4+·TCNQ-·)·1/2TCNQ (solid circle) and (Cs+·TCNQ-·)·1/2TCNQ (circle) in the applied field ranges of (a) ±50 kOe and (b) ±5 kOe at room temperature.