Hiroshi NAKAZAWA (Hiroshima Univ. and IMS), Yoshiko UEDA (Hiroshima Univ.), Keiichi NAKAMURA (Hiroshima Univ.) and Katsuhiko MIYOSHI (Hiroshima Univ.)
[Organometallics 16, 1562 (1997)]
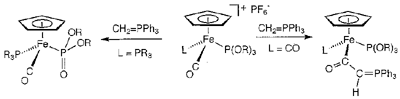
Reactions of PF6- salts of cationic piano stool iron complexes with phosphorus ylide, CH2PPh3, were examined. In the reaction of dicarbonyl complex [Cp(CO)2FeL]+ (L = P(OMe)3, P(OEt)3, PPh2(OMe)), Cp(CO)LFe{C(O)CH=PPh3} is formed by the nucleophilic attack of the carbene carbon of CH2PPh3 on the carbonyl carbon of the complex. In contrast, the reaction of monocarbonyl complex [Cp(CO)LFe{P(OR)3}]+ (L = P(OMe)3, R = Me; L = PMe3, R = Me; L = P(OEt)3, R = Et) yields Cp(CO)LFe{P(O)(OR)2} by the Arbuzov-like dealkylation reaction. [Cp(PMe3)2Fe-{P(OMe)3}]+, having no CO ligand, also exhibits the Arbuzov-like dealkylation reaction under forcing conditions. These results indicate that increasing the back donation ability from a central transition metal to a ligand induces a change in the reaction site from a carbonyl carbon in a CO ligand to an (alpha)-carbon in a phosphite ligand. In the reaction of [Cp(CO)2Fe{PPh2H}]+, proton abstraction from the PPh2H ligand takes place to give a phosphide complex Cp(CO)2FePPh2.
