Hiromi TOBITA (Tohoku Univ. and IMS), Rie SHIOZAWA and Hiroshi OGINO (Tohoku Univ.)
[Chem. Lett. 805 (1997)]
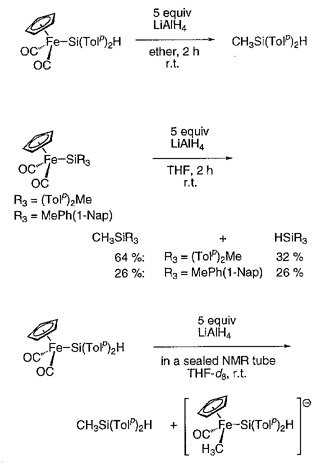
We found that the reaction of LiAlH4 with some silyl(carbonyl)iron complexes resulted in the formation of methylsilanes through the reduction of a carbonyl l igand followed by coupling with the silyl group. Thus, treatment of FpSi(p-Tol)2H (Fp = CpFe(CO)2) with LiAlH4 in ether at room temperature afforded CH3Si(p-Tol)2H in 73% yield. Interestingly, the reaction of FpSi(p-Tol)2H with LiAlD4 exclusively produced CHD2Si(p-Tol)2D, which was characterized by the 1H NMR spectrum showing the Si-CHD2 signal at 0.51 ppm as a quintet (2JHD = 2.0 Hz) and the mass spectrum giving the molecular ion peak at m/z 229. The conversion of a carbonyl ligand in FpSi(p-Tol)2H into a methyl group in CH3Si(p-Tol)2H was further confirmed by the 13C labeling experiments: Reaction of FpSi(p-Tol)2H enriched with 13CO to 32% with LiAlH4 afforded *CH3Si(p-Tol)2H in which the methyl carbon was enriched with 13C. The reaction of silyl complexes without Si-H bonds, namely FpSiR3 (R3 = (p-Tol)2Me, MePh(1-naphthyl)), with LiAlH4 gave CH3SiR3 as a major product, but, in these cases, the simple reduction product HSiR3 was also formed. The NMR tube reaction of FpSi(p-Tol)2H with LiAlH4 in THF-d8 showed the formation of an anionic species [CpFe(CO)(CH3)Si-(p-Tol)2H]- as a main product besides CH3Si(p-Tol)2H. Interestingly, even on heating the reaction mixture to the boiling point of THF-d8, the conversion of the anionic species to CH3Si(p-Tol)2H was not observed.
