Research Theme
Exploring a new application of synchrotron radiation with novel light source technologies
Keywords
synchrotron radiation, accelerator, structured light, coherence, attosecond
UVSOR synchrotron at IMS is a compact low-energy synchrotron radiation facility which has been operating for more than 40 years. The light source performance is still in the word top level and continuous studies on the development of novel light source technologies have been conducted since the 1980s. From a viewpoint of exploring a new application of synchrotron radiation, UVSOR has advantages on the light source performance and the agility to immediately implement new concepts.
The waveform of electromagnetic radiation from an ultra-relativistic electron reflects the motion of the electron. This implies that, by controlling the electron motion in the magnetic field, one can control the properties of the radiation waveform in the nanometer or Angstrom scale. Our group has succeeded in generating the optical vortex beam which has helical phase plane and coherent double-pulse using insertion devices installed in the UVSOR synchrotron. The use of mutual coherence between the double-pulsed components enables time-domain interferometry experiments for controlling and monitoring the quantum state of matter using synchrotron radiation. Such an approach can be applied to the development of new spectroscopic and imaging methods using synchrotron radiation. We aim to develop novel measurement methods and their applications based on manipulating the motion of high-energy electrons in a synchrotron ring.
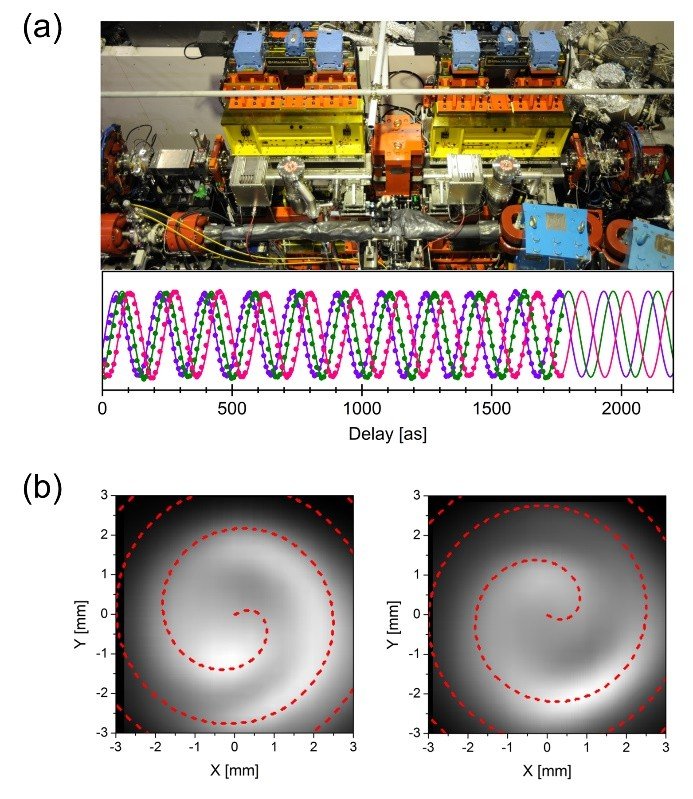
(a) Tandem-undulator system installed in the UVSOR-III synchrotron. Attosecond interference in photoexcitation of helium atoms is attached in the bottom panel. (b) Generation of optical vortex beam by synchrotron radiation.
Selected Publications
- T. Kaneyasu, H. Takeda, K. Hosaka, J. Adachi, “Polarization Measurement of Vacuum Ultraviolet Light using Visible Fluorescence from Neon Atoms”, J. Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena 276, 147488 (2024).
- T. Fuji, T. Kaneyasu, M. Fujimoto, Y. Okano, E. Salehi, M. Hosaka, Y. Takashima, A. Mano, Y. Hikosaka, S.-I. Wada, M. Katoh, “Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction of synchrotron radiation” Optica 10, 302 (2023)
- T. Kaneyasu, Y. Hikosaka, M. Fujimoto, H. Iwayama, M. Katoh, “Electron Wave Packet Interference in Atomic Inner-Shell Excitation”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 113202 (2021)
- Y. Hikosaka, T. Kaneyasu, M. Fujimoto, H. Iwayama, M. Katoh, “Coherent control in the extreme ultraviolet and attosecond regime by synchrotron radiation”, Nature Communications 10, 4988 (2019)
- T. Kaneyasu, Y. Hikosaka, M. Fujimoto, T. Konomi, M. Katoh, H. Iwayama, E. Shigemasa, “Limitations in Photoionization of Helium by an Extreme Ultraviolet Optical Vortex”, Phys. Rev. A 95, 023413, (2017)
- T. Kaneyasu, Y. Takabayashi, Y. Iwasaki, S. Koda, “Beam lifetime study based on momentum acceptance restriction by movable beam scraper”, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 694, 107 (2012)

